Hypertension Self-Care: A Comprehensive Guide
Hypertension, sometimes called high blood pressure, is a long-term medical disorder characterized by consistently raised blood pressure in the arteries. This condition is a significant risk factor for heart disease, stroke, and kidney failure, affecting millions of people worldwide. Given its prevalence and potential severity, understanding and implementing effective hypertension self-care strategies is crucial for managing it and improving overall health. This article will explore various aspects of hypertension self-care, including immediate actions, dietary adjustments, lifestyle changes, and stress management techniques.

Understanding Hypertension
What is Hypertension?
Hypertension occurs when the force of the blood against the artery walls is too high, often requiring the heart to work harder to pump blood. Blood pressure is measured in millimeters of mercury (mm Hg) and recorded as two numbers: systolic pressure (the pressure when the heart beats) over diastolic pressure (the pressure when the heart rests between beats). Normal blood pressure is millimeters per hour, or 120/80. Blood pressure values that continuously surpass 140/90 mm Hg are considered hypertensive.
Causes and Risk Factors
The following are some of the variables that might lead to the development of hypertension:
- Genetics: A family history of high blood pressure raises the danger.
- Unhealthy Diet: High intake of salt, fat, and processed foods can elevate blood pressure.
- Lack of Physical Activity: Increased blood pressure and weight are linked to inactive lifestyles.
- Obesity: Carrying too much weight puts more strain on the heart.
- Alcohol Overindulgence: Consuming large amounts of alcohol regularly may cause blood pressure to rise.
- Chronic Stress: Persistent stress leads to temporary spikes in blood pressure, which can become chronic.
Understanding these causes and risk factors can help develop a comprehensive hypertension self-care plan to manage it effectively.
Hypertension Self-Care: Immediate Steps
Recognizing High Blood Pressure Symptoms
Although hypertension is often asymptomatic, some people may experience symptoms when blood pressure spikes, such as:
- Headaches: in the back of the skull specifically.
- Dizziness: Feeling lightheaded or faint.
- Shortness of breath: Difficulty breathing normally.
- Nosebleeds: Sudden, unexplained nosebleeds.
- Chest Pain: A constriction or tightness in the chest.
Recognizing these symptoms early can prompt immediate action to prevent complications.
Immediate Self-Care Actions
When experiencing high blood pressure symptoms, taking immediate action to lower your blood pressure is essential. These include:
- Relaxation: Sit down and relax in a quiet place.
- Deep Breathing Exercises: Practice deep breathing to reduce stress and lower blood pressure.
- Drink Water: Staying hydrated helps maintain normal blood pressure.
- Avoid Stimulants: Refrain from consuming caffeine or alcohol during a spike.
How to Get Rid of High Blood Pressure in 3 Minutes
While it’s not possible to cure hypertension in three minutes, specific techniques can help lower blood pressure quickly:
- Deep Breathing: Sit comfortably, inhale deeply through your nose, hold for a few seconds, and exhale slowly through your mouth. Repeat several times.
- Cold Water Splash: Splash cold water on your face to stimulate the vagus nerve, which can help lower blood pressure.
- Progressive Muscle Relaxation: Starting from your toes and working your way up to your head, tense and gradually release every muscle group in your body.
7-Second Trick to Lower Blood Pressure
One quick technique to help reduce blood pressure is the 7-second breathing exercise:
- Inhale Slowly: Breathe deeply through your nose for a count of seven seconds.
- Hold: Hold your breath for another count of seven seconds.
- Exhale Slowly: Release the breath slowly through your mouth for a count of seven seconds.
- Repeat this cycle several times to promote relaxation and lower blood pressure.
Diet and Nutrition for Hypertension Self-Care
Hypertension Self-Care Food
A heart-healthy diet is essential for managing hypertension. Make an effort to include the following items in your diet:
- Leafy Greens: Spinach, kale, and lettuce are rich in potassium, which helps balance sodium levels in the body.
- Berries: Antioxidants in raspberries, strawberries, and blueberries promote heart health.
- Oats: Whole grains like oats are high in fiber and can help reduce blood pressure.
- Fatty Fish: Salmon, mackerel, and trout are rich in omega-3 fatty acids, which have been shown to lower blood pressure.

Foods to Avoid
Certain foods can contribute to higher blood pressure and should be limited or avoided:
- Sodium-rich foods: Processed, canned soups and salty snacks can increase blood pressure.
- Sugary Beverages: Sodas and sweetened drinks contribute to weight gain and hypertension.
- Red Meat: High in saturated fats can raise cholesterol and blood pressure.
- Alcohol: Excessive alcohol consumption can negatively affect blood pressure levels.
Creating a Diet Plan Hypertension Self-Care
Creating a personalized diet plan can help manage hypertension self-care effectively. Consider the following steps:
- Consult a Nutritionist: Work with a healthcare professional to develop a diet tailored to your needs.
- Follow DASH Guidelines: The Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension (DASH) diet emphasizes fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins while reducing salt, red meat, and sugar intake.
- Meal Planning: Prepare a food plan to guarantee a well-rounded and nourishing diet.
- Portion Control: Be mindful of portion sizes to avoid overeating and weight gain.
Lifestyle Modifications
Hypertension Self-Care at Home
Implementing lifestyle changes at home is crucial for hypertension self-care. Here are some effective strategies:
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Losing extra weight can considerably lower blood pressure.
- Exercise Regularly: Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise each week, such as brisk walking, cycling, or swimming.
- Quit Smoking: Smoking causes blood pressure to rise and destroys blood vessels. Seek assistance to stop smoking.
- Limit Alcohol: If you consume alcohol, do so sparingly. This translates to one drink for ladies and up to two for males daily.
Physical Activity and Exercise
Regular physical exercise is one of the best strategies to reduce blood pressure and enhance cardiovascular health. Take into account the following advice when adding exercise to your schedule:
- Start Slowly: If you’re new to exercise, start with short sessions and gradually increase the duration and intensity.
- Choose Enjoyable Activities: To stay motivated, engage in activities like dancing, gardening, or playing sports.
- Mix It Up: For a balanced workout, combine aerobic exercises (like walking and swimming) with strength training (like weightlifting and resistance training).
- Monitor Progress: Keep track of your physical activity and progress to stay motivated and on track.
Tricks to Lower Blood Pressure Instantly
In addition to long-term lifestyle changes, there are several tricks to help lower blood pressure instantly:
- Deep Breathing: Slow, deep breaths can help calm the nervous system and reduce blood pressure.
- Hydration: Drinking a glass of water can help maintain blood pressure levels.
- Elevate Feet: Lie down and elevate your feet to improve blood circulation and reduce blood pressure.
Immediate Treatment for High Blood Pressure at Home
If your blood pressure spikes suddenly, you can try these immediate treatments at home:
- Sit Quietly: Find a quiet place to sit and relax.
- Deep Breathing: Practice breathing exercises to lower stress and blood pressure.
- Consume Potassium-Rich Foods: Eat a banana or another potassium-rich snack to help balance sodium levels.
- Avoid Stress: Clear stressful situations and focus on calming activities.
Hypertension Self-Care Activity Level Effects (H-Scale)
The H-Scale is a tool that measures the impact of physical activity levels on hypertension. Engaging in regular physical exercise is essential to keep blood pressure at a healthy level. Use the H-Scale to track your activity and its effects on your blood pressure over time.

Stress Management and Mental Health
Role of Stress in Hypertension
High blood pressure is significantly influenced by ongoing stress. When stressed, your body produces hormones that temporarily increase blood pressure, causing your heart to beat faster and your blood vessels to narrow. Over time, this can lead to long-term hypertension.
Stress Reduction Techniques
Incorporating stress reduction techniques into your daily routine can help in hypertension self-care effectively:
- Yoga: Yoga helps reduce stress and promote relaxation through physical postures, breathing exercises, and meditation.
- Meditation: Daily meditation can help lower stress levels and improve mental health.
- Deep Breathing Exercises: Taking slow, deep breaths helps calm the nervous system and reduce stress.
Incorporating Mindfulness and Relaxation Practices
Mindfulness and relaxation practices are powerful tools for managing stress and hypertension:
- Mindfulness Meditation: Focus on the present moment and practice mindfulness to reduce stress and lower blood pressure.
- Progressive Muscle Relaxation: Tense and slowly relax each muscle group to release tension and promote relaxation.
- Guided Imagery: Visualize a peaceful scene or setting to help calm your mind and reduce stress.
Monitoring and Regular Check-Ups
Importance of Regular Blood Pressure Monitoring
Regularly monitoring your blood pressure at home is essential for hypertension self-care. It helps you:
- Track Progress: Monitor the effectiveness of your self-care efforts and make necessary adjustments.
- Detect Changes: Identify sudden changes in blood pressure that may require medical attention.
- Stay Informed: For better management, inform your healthcare provider about your blood pressure levels.
When to See a Doctor
Despite your best self-care efforts, there are times when you should consult a healthcare professional:
- Consistently High Readings: If your blood pressure readings are consistently above 140/90 mm Hg.
- Severe Symptoms: Experiencing severe headaches, chest pain, or difficulty breathing.
- Medication Management: If you need advice on medication or adjustments to your current prescription.
- Regular Check-Ups: Schedule regular check-ups to monitor your condition and receive professional guidance.
Conclusion
Hypertension self-care involves a combination of immediate actions, dietary changes, lifestyle modifications, stress management, and regular monitoring. These practices can effectively control your blood pressure and improve your overall health. Remember, consistency and commitment to these self-care strategies are crucial to achieving long-term success in managing hypertension.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about Hypertension Self-Care
Q. What are the most effective lifestyle changes for hypertension self-care?
A: The most effective lifestyle changes for hypertension self-care include adopting a heart-healthy diet, engaging in regular physical activity, maintaining a healthy weight, reducing sodium intake, limiting alcohol consumption, and quitting smoking. The DASH (Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension) diet is particularly effective, emphasizing fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins while minimizing salt and sugar intake. Regular exercise, such as brisk walking, cycling, or swimming for at least 150 minutes per week, also significantly helps lower blood pressure.
Q. Can stress management techniques help in lowering blood pressure?
A: Stress management techniques can significantly help lower blood pressure. Chronic stress is a known contributor to hypertension, and managing stress through techniques like deep breathing exercises, meditation, yoga, and mindfulness can promote relaxation and reduce blood pressure. Practices like progressive muscle relaxation and guided imagery also help reduce stress and improve overall mental well-being, contributing to better blood pressure control.
Q. What immediate actions can I take if my blood pressure spikes?
A: If your blood pressure spikes, immediate actions you can take include sitting down and relaxing in a quiet place, practising deep breathing exercises, and drinking a glass of water. You can also try elevating your feet to improve blood circulation. Potassium-rich foods like bananas or avocados can help balance sodium levels and reduce blood pressure. Avoiding stressful situations and focusing on calming activities can also help manage a sudden increase in blood pressure.
Q. What foods should I avoid for effective hypertension self-care?
A: To manage hypertension self-care effectively, it is essential to avoid foods high in sodium, such as processed foods, canned soups, and salty snacks. Limit sugary beverages like sodas and sweetened drinks, as they contribute to weight gain and increased blood pressure. Red meat is high in saturated fats, and excessive alcohol consumption should also be avoided. Instead, focus on a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins to maintain healthy blood pressure levels.
Q. How often should I monitor my blood pressure at home?
A: It is recommended that you monitor your blood pressure at home regularly, ideally once a day at the same time. Keeping a log of your readings can help you track your progress and identify any patterns or changes in your blood pressure. Regular monitoring is crucial for managing hypertension self-care effectively and can provide valuable information for your healthcare provider. If you notice consistently high readings or significant changes, it is essential to consult your doctor for further evaluation and guidance.

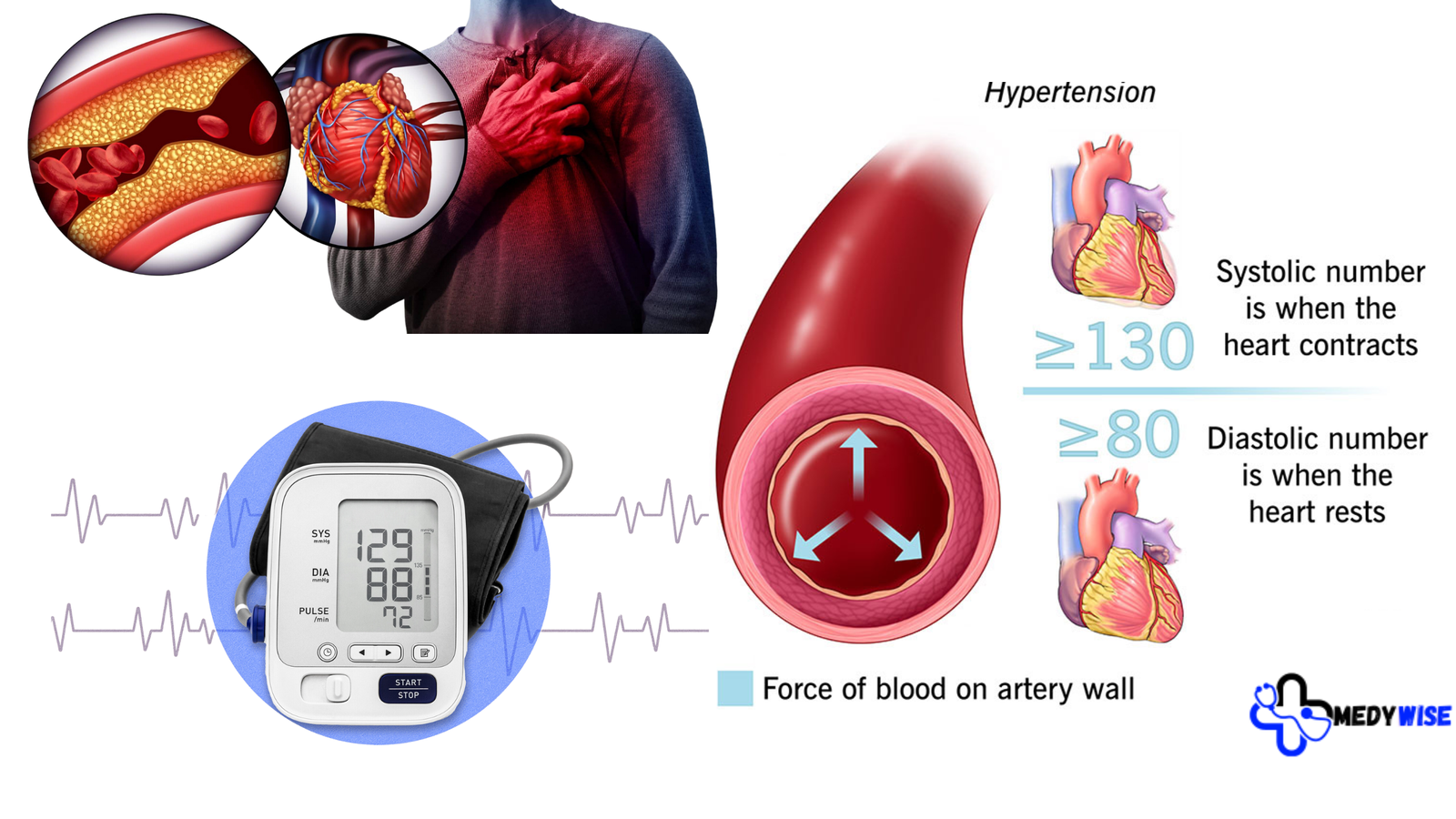
[…] throughout the day can help maintain proper hydration and prevent the onset of dehydration-induced high blood pressure. Individuals, especially those with a history of blood pressure issues, should monitor their […]