Introduction
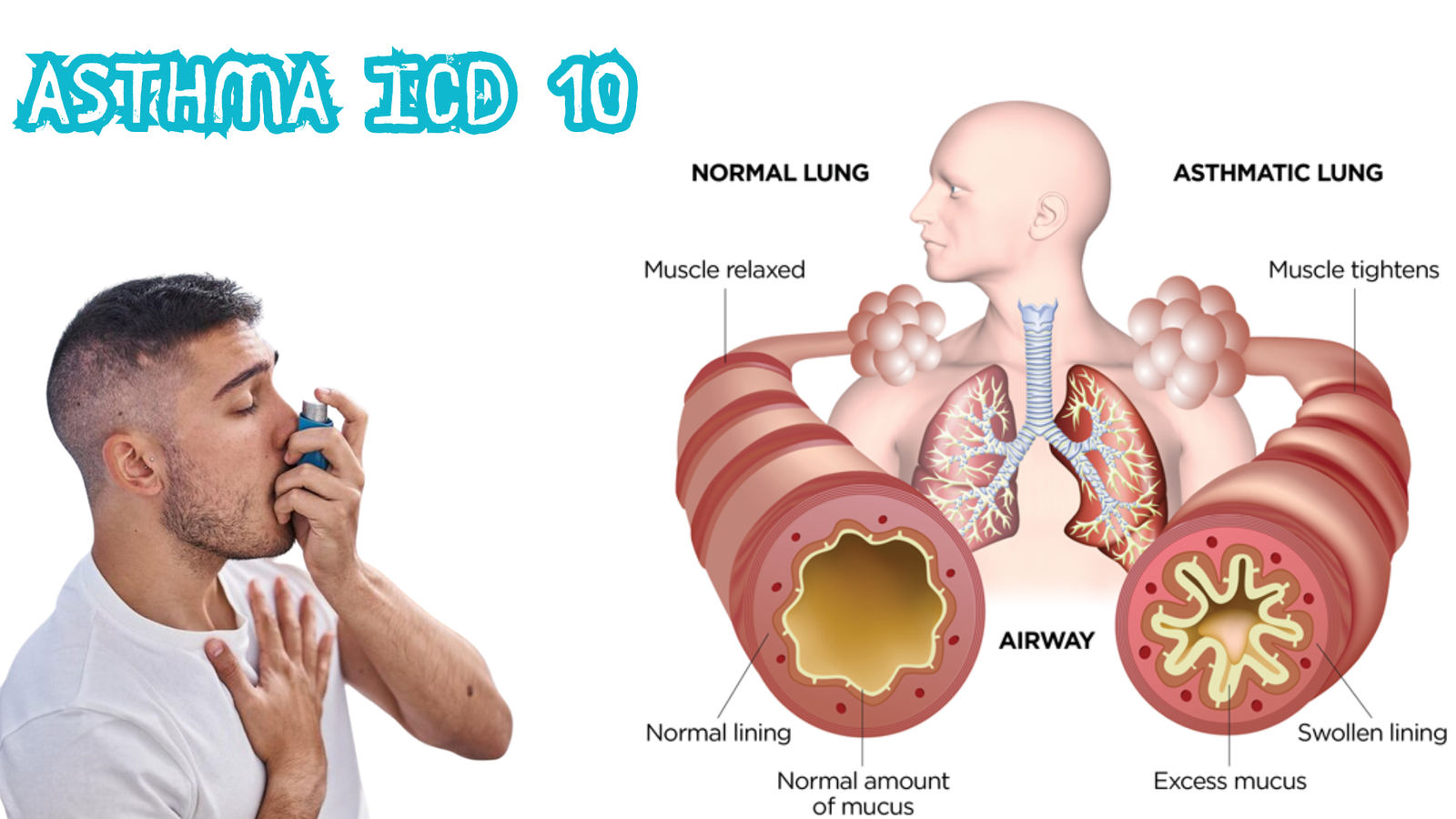
Asthma, a chronic respiratory condition characterized by episodes of airway narrowing, inflammation, and hyperreactivity, significantly impacts millions of individuals worldwide. Effective management of this prevalent disease hinges on a comprehensive understanding of its classification and documentation, primarily through the International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision (ICD-10). This detailed guide aims to provide healthcare professionals and caregivers with essential insights into managing asthma using the “asthma ICD 10” codes, facilitating precise diagnosis, treatment, and overall patient care.
Understanding Asthma and Its ICD-10 Classification
Asthma is a prevalent condition affecting millions worldwide, with varying degrees of severity and frequency of symptoms. The ICD-10 coding system is crucial for accurately documenting and managing asthma. By utilizing the asthma ICD 10 codes, healthcare providers can ensure that each patient receives personalized care tailored to the severity and specifics of their condition, thereby optimizing treatment approaches and improving patient outcomes.
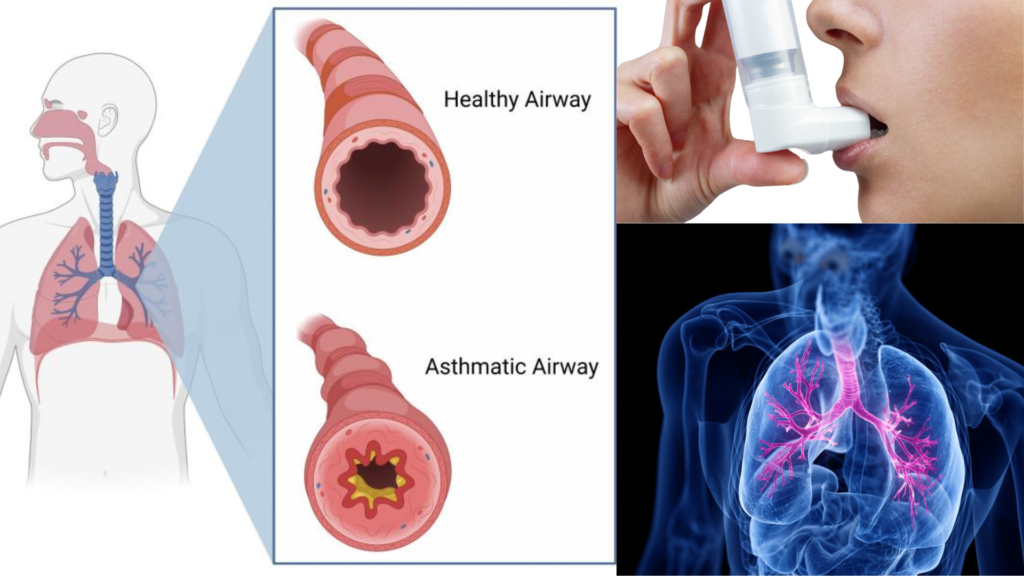
What is the ICD-10 Code for Asthma?
The primary ICD-10 code for asthma is J45. This code encompasses various types of asthma, each with its specific subcategories based on the severity and frequency of symptoms. Utilizing the correct asthma ICD 10 code ensures patients receive the appropriate resources and treatments for managing their condition effectively.
J45 ICD-10: The Core Code for Asthma
J45 is the central code for asthma, which further branches into more specific codes to describe different types and severities of asthma. Understanding these subcategories is vital for accurate diagnosis and management. Precise use of asthma ICD 10 codes aids in epidemiological studies, healthcare planning, and ensuring patients have access to the necessary healthcare services.
Asthma Unspecified ICD-10
J45.909 is the code for unspecified asthma. This code is used when the specific type of asthma is not determined or documented. Healthcare providers must avoid using unspecified codes whenever possible by accurately diagnosing the type of asthma. Proper documentation using specific asthma ICD 10 codes helps track treatment efficacy and improve patient care protocols.
Asthma Exacerbation ICD-10
J45.901 is the code for asthma with acute exacerbation. An exacerbation is a sudden worsening of asthma symptoms that requires immediate medical attention. Accurate coding of exacerbations with the asthma ICD 10 is crucial for treatment planning, emergency response, and monitoring of patient progress during recovery.
Childhood Asthma ICD 10
Childhood asthma is coded similarly to adult asthma but may require additional considerations for accurate documentation and management. Pediatric asthma often presents differently; understanding the nuances is vital for adequate care. Precise use of asthma ICD 10 codes in pediatric cases ensures that young patients receive the most effective treatments and interventions to improve their long-term health and quality of life.
Common Asthma-Related ICD-10 Codes
Wheezing ICD-10
R06.2 is the code for wheezing, a common symptom of asthma. While wheezing can occur in various conditions, its association with asthma is significant for proper diagnosis and treatment. Recognizing wheezing as a symptom and correlating it with asthma using the asthma ICD 10 codes can facilitate a more targeted approach to managing the respiratory distress often seen in asthmatic patients.
What is Asthma ICD 10 J45 0?
J45.0 refers to predominantly allergic asthma, also known as extrinsic asthma. This type is triggered by common allergens such as pollen, dust mites, and pet dander. Identifying this specific asthma ICD 10 code helps healthcare providers tailor treatment plans that include pharmacological interventions and environmental management strategies.
What is the ICD-10 Code for J45 9?
J45.9 includes other and unspecified asthma types. Striving for more specific coding is crucial to ensuring accurate treatment and monitoring. This category highlights the need for thorough diagnostic processes to avoid the potential pitfalls of under-treating or mismanaging asthma cases.
What is the ICD-10 Code for J45998?
J45.998 is the code for other asthma with other complications. This code is used when asthma presents with additional complications not classified elsewhere, such as cardiovascular or neurological conditions. This asthma ICD 10 code prompts clinicians to consider a comprehensive treatment approach addressing all patient health facets.

Main ICD-10 Codes for Asthma
- J45 – Asthma: This is the primary code for asthma and includes various subcategories. It is the foundation for all asthma-related diagnosis and management in clinical settings.
- J45.0—Predominantly allergic asthma: Also known as extrinsic asthma, allergens trigger this type. Effective management includes allergen avoidance and control of inflammation.
- J45.1 – Nonallergic asthma: Also known as intrinsic asthma, allergens do not trigger this type. It often requires a focus on controlling symptoms and maintaining airway function.
- J45.8—Mixed asthma: This code is used when allergic and nonallergic factors contribute to asthma. Treatment may involve a combination of strategies for both allergic and nonallergic asthma.
- J45.9 – Asthma, unspecified: This code is used when the specific type of asthma is not documented. Precise diagnosis is encouraged to apply the most effective treatments.
Detailed Breakdown of Asthma ICD 10 Codes
To provide more detailed information, additional codes are used to specify the severity and level of asthma control:
- J45.20 – Mild intermittent asthma: Characterized by brief flare-ups, this type may require less frequent medication.
- J45.21 – Mild persistent asthma: Symptoms are more consistent, but control is generally manageable with low-dose treatments.
- J45.22 – Moderate persistent asthma: Daily symptoms require more aggressive treatment to maintain control.
- J45.23 – Severe persistent asthma: Continuous, severe symptoms necessitate high-level management strategies, including possible specialized therapies.
- J45.30 – Uncomplicated asthma: Asthma can be managed with standard treatment protocols without frequent exacerbations.
- J45.31 – Acute exacerbation of asthma: Indicates a sudden and severe increase in symptoms requiring urgent care.
- J45.32 – Status asthmaticus: A severe condition where asthma is unresponsive to initial treatments and poses a risk for significant complications.

Additionally, J45.901 is designated for asthma with acute exacerbation, a severe and sudden worsening of symptoms, emphasizing the need for immediate medical attention. This detailed understanding of asthma ICD 10 codes helps ensure that each patient receives optimal care tailored to their needs.
Significance of ICD-10 in Asthma Management
ICD-10 codes are vital for several reasons:
- Accurate Diagnosis: They enable precise documentation of asthma and its various types, aiding in accurate diagnosis and treatment. Utilizing the correct asthma ICD 10 codes ensures that each patient’s asthma type is accurately identified, which is crucial for selecting the most effective treatment plans.
- Data Collection and Research: ICD-10 codes facilitate data collection, enabling research on asthma prevalence, trends, and outcomes. By standardizing how asthma cases are recorded, researchers can generate reliable data contributing to global efforts to understand and combat asthma.
- Billing and Reimbursement: These codes are essential for healthcare providers to receive reimbursement for services rendered. Proper use of asthma ICD 10 codes ensures that healthcare facilities are adequately compensated for managing asthma, which can be resource-intensive.
- Public Health Monitoring: ICD-10 codes help monitor public health trends and plan interventions. They allow health authorities to track asthma incidence and prevalence, helping allocate resources effectively and design targeted public health interventions.
Challenges and Solutions in Asthma ICD 10 Implementation
Common Challenges
- Complexity of Codes: The detailed nature of ICD-10 codes can be challenging for healthcare providers to navigate, leading to potential errors in documentation. The specificity required can sometimes lead to inaccuracies if not understood fully.
- Training and Education: Healthcare providers must receive adequate training and education to use ICD-10 codes effectively. Without proper training, adopting these codes can be slow and error-prone.
- Integration with Electronic Health Records (EHR): Ensuring seamless integration of ICD-10 codes with EHR systems can be complex and time-consuming. Technical difficulties may arise, complicating the recording processes and potentially leading to data entry errors.
Solutions
- Comprehensive Training Programs: Implementing comprehensive training programs for healthcare providers can enhance their understanding and use of ICD-10 codes. These programs should include hands-on sessions, case studies, and continuous education opportunities to keep providers updated on the latest coding practices.
- User-Friendly Tools and Resources: Developing user-friendly tools and resources, such as coding guides and online databases, can assist healthcare providers in accurate coding. These tools can simplify the process, reduce the likelihood of errors, and improve coding efficiency in everyday clinical practice.
- EHR Integration: Collaborating with EHR vendors to ensure seamless integration of ICD-10 codes can streamline the documentation process and improve accuracy. This involves regular updates to EHR systems to accommodate changes in ICD-10 codes and ensure that these systems are user-friendly for clinical staff.
By addressing these challenges with practical solutions, healthcare systems can enhance the reliability and efficiency of asthma management through the use of ICD-10 codes, ultimately leading to better patient outcomes and more efficient use of healthcare resources.
Future Directions in Asthma Management and ICD-10
Advances in Technology
Technological advancements are poised to revolutionize asthma management. Integrating ICD-10 codes with advanced data analytics, telemedicine, and mobile health applications can enhance patient monitoring, improve adherence to treatment plans, and provide real-time feedback to healthcare providers. For instance, mobile apps that track symptoms and medication use can be integrated with ICD-10 codes to offer personalized recommendations and alerts. This integration can facilitate better tracking of asthma management outcomes and trends over time, leading to more informed decisions and personalized care strategies. Future technologies may also include AI-driven predictive models that use ICD-10 data to forecast asthma attacks, allowing preemptive management adjustments.
Precision Medicine
Precision medicine aims to tailor medical treatment to individual characteristics, including genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors. In asthma management, precision medicine can leverage ICD-10 codes to identify specific phenotypes and endotypes, enabling targeted therapies. For example, patients with severe allergic asthma (J45.0) may benefit from biologic therapies targeting particular immune pathways. This approach can be further enhanced by using ICD-10 codes to systematically track patient responses to tailored treatments, refining and personalizing therapeutic strategies over time. Additionally, genomic data linked with asthma ICD 10 codes could lead to the discovery of novel therapeutic targets and better classification of asthma types.
Global Health Initiatives
Global health initiatives are essential for addressing the burden of asthma, particularly in low- and middle-income countries. ICD-10 codes can play a crucial role in these initiatives by providing standardized data for monitoring asthma prevalence, identifying disparities in care, and planning interventions. Collaborative efforts among governments, healthcare organizations, and communities can improve access to asthma care and reduce the global disease burden. Enhanced use of ICD-10 codes in global health databases can aid in allocating resources where they are most needed and evaluating intervention strategies across different populations. Further, international cooperation on asthma management protocols, facilitated by uniform ICD-10 coding, can lead to more effective and scalable public health responses.

Expanding on these future directions, it is clear that ICD-10 codes are foundational for current asthma management practices and will also be integral to the evolution of how asthma is understood and treated globally. Integrating technology, precision medicine, and global health initiatives with ICD-10 coding practices promises a future where asthma care is more effective, personalized, and universally accessible.
Conclusion
Effective asthma management relies heavily on precisely using “asthma ICD 10” codes. These codes facilitate accurate diagnosis and tailored treatment plans and contribute to the healthcare system’s broader understanding and management of asthma. By mastering the ICD-10 coding for asthma, healthcare professionals can offer high-quality, personalized care, improving patient outcomes and advancing global health initiatives. As technology and medical strategies evolve, the potential for enhanced asthma management through the adept use of “asthma ICD 10” codes is vast and promising. Through continued education, collaboration, and innovation, healthcare providers can ensure optimal care for individuals with this challenging condition.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Asthma ICD 10 Codes
Q. What is the primary ICD-10 code for asthma?
A: The primary ICD-10 code for asthma is J45. This code serves as a general category for asthma diagnoses and includes various subcategories to reflect the type and severity of the condition. Using this code helps healthcare providers standardize diagnoses, treatments, and billing processes across different cases of asthma.
Q. What does asthma ICD 10 J45.0 represent?
A: J45.0 represents predominantly allergic asthma, also known as extrinsic asthma. This type of asthma is triggered by exposure to external allergens such as pollen, dust mites, or pet dander. Identifying this specific type using the J45.0 code is crucial for implementing targeted treatment strategies, like allergen avoidance and specific immunotherapy.
Q. How is asthma exacerbation coded in ICD-10?
A: In the ICD-10 system, asthma exacerbation is specifically coded as J45.901. This code denotes an acute exacerbation, where asthma symptoms suddenly become worse and more severe. This coding is essential for highlighting the urgency and immediate need for medical intervention to manage the exacerbation effectively.
Q. How should childhood asthma be documented?
A: Childhood asthma should be documented using the same ICD-10 codes as adult asthma but with additional considerations to account for the age-specific aspects of the disease. It’s important to note the onset age and possible environmental or developmental factors that might influence asthma’s progression and management in children.
Q. What is the significance of specifying asthma types in ICD-10?
A: Specifying asthma types in the ICD-10 codes, such as distinguishing between allergic (J45.0) and non-allergic (J45.1) asthma, is critical for several reasons. It enables personalized treatment plans that are tailored to each patient’s specific triggers and mechanisms of asthma. Accurate specification also aids in tracking treatment efficacy and outcomes, improving patient management, and facilitating relevant research and public health reporting.